Environment Sustainability is a fundamental part of our mission, guiding how we operate. We reduce our environmental impact through practices that enrich and support the natural environment.
What is Green Thread?
Through Green Thread, our environment sustainability platform, we bring innovative and efficient solutions to life. We are passionately focused on reducing the environmental impact within our operations. We continuously improve our own practices, while offering expertise and practical solutions.
We place special emphasis on responsible sourcing, waste minimization, efficient operations, and transportation management. But we don't stop there. We measure our impact and hold ourselves accountable to continuously improve.
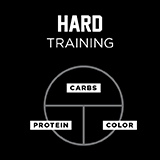
Training Plate
Each plate is associated with a type of training–easy, moderate, or hard. But it is always important to recognize that there is no one-size-fits-all when fueling your body. Your sport and position, training environment, and body composition are a few ways that determine your unique needs.
Fueling your body is critical for preventing injury, optimal performance, and maintaining daily activities. Your fat and hydration consumption should increase as your training increases.
- Easy can be applied to an easy workout, cross-training, or rest days
- Moderate is your typical workout and practice days and acts as the baseline. Adjust meals based on your needs and your body’s response.
- Hard days require more energy from carbs to fuel, refuel and refresh your body. This plate is for before and after events, when timed correctly.
Training Type and Meal Components
CARBS: Carbohydrates are the primary fuel source for our bodies for moderate to high-intensity exercise. Helps with:
- Muscle contraction
- Maintaining energy levels
- Fuels our brain and muscles throughout the day.
PROTEIN: Unlike carbohydrates or fats, we can’t store protein in our bodies. Regularly consuming adequate amounts of protein ensures we are replenishing the availability of this nutrient. Protein supports:
- Metabolism
- Immune function
- Weight
- Athletic performance
COLORS: Also known as fruits & vegetables:
- Offer a variety of vitamins and minerals for normal function, growth, and maintenance.
THE ICONS: Use these tools to make intentional choices with regards to carbs, protein, and colors while dining on campus.
- Look for these icons on the online menu!